
WHO warns of falsified Augmentin
| THE INDEPENDENT | The World Health Organisation (WHO) has warned that fake versions of the antibiotic Augmentin have been discovered in Uganda and Kenya.
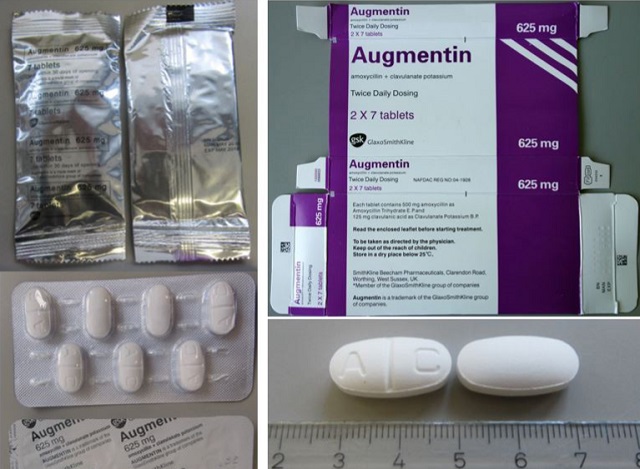
The genuine drug is sold by GlaxoSmithKline but the packaging of the falsified drugs says it is manufactured by SmithKline Beecham Ltd. The manufacture date is August 2016 and expiry date is August 2019. The batch number 786627 and is in 14-count packs purporting to contain 625mg tablets.
But WHO says it does not contain the active ingredient found in amoxicillin trihydrate and potassium clavulanate which is the base for the genuine Augmentin manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline.
Augmentin is an important drug because WHO has it on its list of essential medicines. It is a commonly-used treatment for bacterial infections. Last year, the WHO issued a similar alert after finding falsified versions of the drug in Cameroon.
WHO says it was informed by the Uganda National Drug Authority that falsified Augmentin had been discovered through routine post marketing surveillance on the quality of medical products in the market. Sample testing revealed none of the expected active ingredients.
The National Drug Authority on July 25 showed journalists in Kampala several substandard and counterfeit drugs that are being circulated in the market, including Augmentin. The other were Postinor 2 (Levonogestre) and Quinine Bisulphate.
Nasser Lubowa, the NDA head of post-market surveillance urged the public to be vigilant when buying medicines and report suspicious cases to NDA.
Meanwhile, the Kenya Pharmacy and Poisons Board confirmed that the same batch of falsified Augmentin had previously been found at patient level in Kenya.
Augmentin (Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium) is a prescription antibiotic used to treat infections caused by bacteria. It belongs to the penicillin class of antibiotics and contains two drugs: amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. This combination makes Augmentin work against more types of bacteria than antibiotics that contain amoxicillin alone.
It is effective for treating pneumonia, ear infections, sinus infections, skin infections, and urinary tract infections. It comes in three forms, all of which are taken by mouth: immediate-release tablet, extended-release tablet, and liquid suspension.
Augmentin is available in a generic form as Amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium.
According to a report in the Business Standard newspaper of India, the Delhi High Court in June restrained a pharma company called Anglo-French Drugs and Industries Ltd (AFDIL) from advertising or marketing a drug which is deceptively similar to Glaxo Group’s Augmentin.
The court asked AFDIL not to use or deal in any goods with the same trade dress or packaging which is deceptively similar to Glaxo’s packaging or any other deceptively variant.
The WHO said the falsified drug found in Uganda and Kenya is very similar in packaging to the genuine drug sold by GlaxoSmithKline.
In India, AFDIL had sought to sell a similar drug advertised and marketed under the business mark ‘Anglomentin’ / ‘Anglomentin Duo’. GlaxoSmithKline sells its medicine trademarked as ‘Augmentin’ / ‘Augmentin Duo’.
Glaxo, in its suit, also sought to restrain AFDIL from selling or dealing with products and services in packaging which is deceptively similar to its green and white product packaging, trade dress and colour combination thus, amounting to passing off the products as those of Glaxo.
It said it got to know about the defendant’s products in June 2019 and the drugs of both Glaxo and AFDIL were being used for same diseases and have same active ingredients.
The court noted that the trademark being used by AFDIL is deceptively similar to that of Glaxo. It noted that Glaxo adopted the trademark Augmentin in 1967 whereas AFDIL started using the trademark in or around in 2019.
****
 The Independent Uganda: You get the Truth we Pay the Price
The Independent Uganda: You get the Truth we Pay the Price



